搜索到
1
篇与
的结果
-
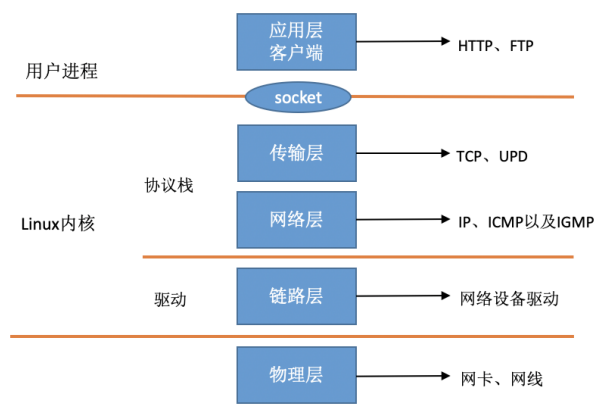
![How to receive a network packet in Linux]() How to receive a network packet in Linux {collapse}{collapse-item label=" 一、简介 " open}在TCP/IP ⽹络分层模型⾥,整个协议栈被分成了物理层、链路层、⽹络层,传输层和应⽤层。物理层对应的是⽹卡和⽹线,应⽤层对应的是我们常⻅的 Nginx,FTP 等等各种应⽤。Linux 实现的是链路层、⽹络层和传输层这三层。在 Linux 内核实现中,链路层协议靠⽹卡驱动来实现,内核协议栈来实现⽹络层和传输层。内核对更上层的应⽤层提供 socket 接⼝来供⽤户进程访问。在 Linux 的源代码中,⽹络设备驱动对应的逻辑位于 driver/net/ethernet , 其中 intel 系列⽹卡的驱动在 driver/net/ethernet/intel ⽬录下。协议栈模块代码位于 kernel 和 net ⽬录。{lamp/}此Linux中断处理函数是分上半部和下半部的。上半部是只进⾏最简单的⼯作,快速处理然后释放 CPU ,接着 CPU 就可以允许其它中断进来。剩下将绝⼤部分的⼯作都放到下半部中。2.4 以后的内核版本采⽤的下半部实现⽅式是软中断,由 ksoftirqd 内核线程全权处理。和硬中断不同的是,硬中断是通过给 CPU 物理引脚施加电压变化,⽽软中断是通过给内存中的⼀个变量的⼆进制值以通知软中断处理程序。当⽹卡上收到数据以后,Linux 中第⼀个⼯作的模块是⽹络驱动。 ⽹络驱动会以 DMA 的⽅式把⽹卡上收到的帧写到内存⾥。再向 CPU 发起⼀个中断,以通知 CPU 有数据到达。第⼆,当 CPU 收到中断请求后,会去调⽤⽹络驱动注册的中断处理函数。 ⽹卡的中断处理函数并不做过多⼯作,发出软中断请求,然后尽快释放 CPU。ksoftirqd 检测到有软中断请求到达,调⽤ poll 开始轮询收包,收到后交由各级协议栈处理。对于 udp 包来说,会被放到⽤户 socket 的接收队列中。{/collapse-item}{collapse-item label=" 二、linux启动 " open} 1. 创建ksoftirqd内核进程 系统初始化的时候在 kernel/smpboot.c中调⽤了 smpboot_register_percpu_thread, 该函数进⼀步会执⾏到 spawn_ksoftirqd(位于kernel/softirq.c)来创建出 softirqd 进程。//file: kernel/softirq.c static struct smp_hotplug_thread softirq_threads = { .store = &ksoftirqd, .thread_should_run = ksoftirqd_should_run, .thread_fn = run_ksoftirqd, .thread_comm = "ksoftirqd/%u", }; static __init int spawn_ksoftirqd(void) { register_cpu_notifier(&cpu_nfb); BUG_ON(smpboot_register_percpu_thread(&softirq_threads)); return 0; } early_initcall(spawn_ksoftirqd);2. 网络子系统初始化 //file: net/core/dev.c static int __init net_dev_init(void) { ...... for_each_possible_cpu(i) { struct softnet_data *sd = &per_cpu(softnet_data, i); memset(sd, 0, sizeof(*sd)); skb_queue_head_init(&sd->input_pkt_queue); skb_queue_head_init(&sd->process_queue); sd->completion_queue = NULL; INIT_LIST_HEAD(&sd->poll_list); ...... } ...... open_softirq(NET_TX_SOFTIRQ, net_tx_action); open_softirq(NET_RX_SOFTIRQ, net_rx_action); } subsys_initcall(net_dev_init);2.1 linux 内核通过调⽤ subsys_initcall 来初始化各个⼦系统,在源代码⽬录⾥你可以 grep 出许多对这个函数的调⽤。2.2 网络子系统初始化的时候会为每个 CPU 都申请⼀个 softnet_data 数据结构,在这个数据结构⾥的poll_list 是等待驱动程序将其 poll 函数注册进来。2.3 open_softirq 注册了每⼀种软中断都注册⼀个处理函数, NET_TX_SOFTIRQ 的处理函数为net_tx_action,NET_RX_SOFTIRQ 的为 net_rx_action。open_softirq 注册的⽅式是记录在 softirq_vec 变量⾥的。ksoftirqd 线程收到软中断的时候,也会使⽤这个变量来找到每⼀种软中断对应的处理函数。3. 协议栈注册 内核实现了网络层的IP协议、传输层的TCP协议和UDP协议,这些协议对应的实现函数分别是 ip_rcv(), tcp_v4_rcv()和 udp_rcv()。内核是通过注册的⽅式来实现的, Linux 内核中的 fs_initcall 和 subsys_initcall 类似,也是初始化模块的⼊⼝。 fs_initcall 调⽤ inet_init 后开始⽹络协议栈注册。 通过 inet_init ,将这些函数注册到了 inet_protos 和 ptype_base 数据结构中了。//file: net/ipv4/af_inet.c static struct packet_type ip_packet_type __read_mostly = { .type = cpu_to_be16(ETH_P_IP), .func = ip_rcv, }; static const struct net_protocol udp_protocol = { .handler = udp_rcv, .err_handler = udp_err, .no_policy = 1, .netns_ok = 1, }; static const struct net_protocol tcp_protocol = { .early_demux = tcp_v4_early_demux, .handler = tcp_v4_rcv, .err_handler = tcp_v4_err, .no_policy = 1, .netns_ok = 1, }; static int __init inet_init(void) { ...... if (inet_add_protocol(&icmp_protocol, IPPROTO_ICMP) < 0) pr_crit("%s: Cannot add ICMP protocol\n", __func__); if (inet_add_protocol(&udp_protocol, IPPROTO_UDP) < 0) pr_crit("%s: Cannot add UDP protocol\n", __func__); if (inet_add_protocol(&tcp_protocol, IPPROTO_TCP) < 0) pr_crit("%s: Cannot add TCP protocol\n", __func__); ...... dev_add_pack(&ip_packet_type); }inet_protos 记录着 udp,tcp 的处理函数地址,ptype_base 存储着 ip_rcv() 函数的处理地址4. ⽹卡驱动初始化 每⼀个驱动程序(不仅仅只是⽹卡驱动)会使⽤ module_init 向内核注册⼀个初始化函数,当驱动被加载时,内核会调⽤这个函数。//file: drivers/net/ethernet/intel/igb/igb_main.c static struct pci_driver igb_driver = { .name = igb_driver_name, .id_table = igb_pci_tbl, .probe = igb_probe, .remove = igb_remove, ...... }; static int __init igb_init_module(void) { ...... ret = pci_register_driver(&igb_driver); return ret; }第2步中驱动probe让驱动处于ready第5步中⽹卡驱动实现了 ethtool 所需要的接⼝,也在这⾥注册完成函数地址的注册。当ethtool 发起⼀个系统调⽤,内核会找到对应操作回调函数第6步注册的 igb_netdev_ops 中包含的是 igb_open 等函数,该函数在⽹卡被启动的时候会被调⽤5. 启动⽹卡 当上⾯的初始化都完成以后,就可以启动⽹卡了。//file: drivers/net/ethernet/intel/igb/igb_main.c static int __igb_open(struct net_device *netdev, bool resuming) { /* allocate transmit descriptors */ err = igb_setup_all_tx_resources(adapter); /* allocate receive descriptors */ err = igb_setup_all_rx_resources(adapter); /* 注册中断处理函数 */ err = igb_request_irq(adapter); if (err) goto err_req_irq; /* 启⽤NAPI */ for (i = 0; i < adapter->num_q_vectors; i++) napi_enable(&(adapter->q_vector[i]->napi)); ...... }{/collapse-item}{collapse-item label=" 二、收包流程 " open} 1. 硬中断处理 ⾸先当数据帧从⽹线到达⽹卡上的时候,第⼀站是⽹卡的接收队列。⽹卡在分配给⾃⼰的 RingBuffer中寻找可⽤的内存位置,找到后 DMA 引擎会把数据 DMA 到⽹卡之前关联的内存⾥,这个时候 CPU都是⽆感的。当 DMA 操作完成以后,⽹卡会向 CPU 发起⼀个硬中断,通知 CPU 有数据到达。2. ksoftirqd 内核线程处理软中断 内核线程初始化的时候,我们介绍了 ksoftirqd 中两个线程函数 ksoftirqd_should_run 和run_ksoftirqd 。static int ksoftirqd_should_run(unsigned int cpu) { return local_softirq_pending(); } #define local_softirq_pending() \ __IRQ_STAT(smp_processor_id(), __softirq_pending)这⾥看到和硬中断中调⽤了同⼀个函数 local_softirq_pending 。使⽤⽅式不同的是硬中断位置是为了写⼊标记,这⾥仅仅只是读取。如果硬中断中设置了 NET_RX_SOFTIRQ ,这⾥⾃然能读取的到。static void run_ksoftirqd(unsigned int cpu) { local_irq_disable(); if (local_softirq_pending()) { __do_softirq(); rcu_note_context_switch(cpu); local_irq_enable(); cond_resched(); return; } local_irq_enable(); }在 __do_softirq 中,判断根据当前 CPU 的软中断类型,调⽤其注册的 action ⽅法。asmlinkage void __do_softirq(void) { do { if (pending & 1) { unsigned int vec_nr = h - softirq_vec; int prev_count = preempt_count(); ... trace_softirq_entry(vec_nr); h->action(h); trace_softirq_exit(vec_nr); ... } h++; pending >>= 1; } while (pending); }硬中断中设置软中断标记,和 ksoftirq 的判断是否有软中断到达,都是基于smp_processor_id() 的。这意味着只要硬中断在哪个 CPU 上被响应,那么软中断也是在这个 CPU 上处理的。如果你发现你的 Linux 软中断 CPU 消耗都集中在⼀个核上的话,做法是要把调整硬中断的 CPU 亲和性,来将硬中断打散到不同的 CPU 核上去。//file:net/core/dev.c static void net_rx_action(struct softirq_action *h) { struct softnet_data *sd = &__get_cpu_var(softnet_data); unsigned long time_limit = jiffies + 2; int budget = netdev_budget; void *have; local_irq_disable(); while (!list_empty(&sd->poll_list)) { ...... n = list_first_entry(&sd->poll_list, struct napi_struct, poll_list); work = 0; if (test_bit(NAPI_STATE_SCHED, &n->state)) { work = n->poll(n, weight); trace_napi_poll(n); } budget -= work;net_rx_action } }函数开头的 time_limit 和 budget 是⽤来控制 net_rx_action 函数主动退出的,⽬的是保证⽹络包的接收不霸占 CPU 不放。 等下次⽹卡再有硬中断过来的时候再处理剩下的接收数据包。其中 budget 可以通过内核参数调整。 这个函数中剩下的核⼼逻辑是获取到当前 CPU 变量 softnet_data,对其 poll_list进⾏遍历, 然后执⾏到⽹卡驱动注册到的 poll 函数。对于 igb ⽹卡来说,就是 igb 驱动⾥的igb_poll 函数了。/** * igb_poll - NAPI Rx polling callback * @napi: napi polling structure * @budget: count of how many packets we should handle **/ static int igb_poll(struct napi_struct *napi, int budget) { ... if (q_vector->tx.ring) clean_complete = igb_clean_tx_irq(q_vector); if (q_vector->rx.ring) clean_complete &= igb_clean_rx_irq(q_vector, budget); ... }在读取操作中, igb_poll 的重点⼯作是对 igb_clean_rx_irq 的调⽤。static bool igb_clean_rx_irq(struct igb_q_vector *q_vector, const int budget) { ... do { /* retrieve a buffer from the ring */ skb = igb_fetch_rx_buffer(rx_ring, rx_desc, skb); /* fetch next buffer in frame if non-eop */ if (igb_is_non_eop(rx_ring, rx_desc)) continue; } /* verify the packet layout is correct */ if (igb_cleanup_headers(rx_ring, rx_desc, skb)) { skb = NULL; continue; } /* populate checksum, timestamp, VLAN, and protocol */ igb_process_skb_fields(rx_ring, rx_desc, skb); napi_gro_receive(&q_vector->napi, skb); }igb_fetch_rx_buffer 和 igb_is_non_eop 的作⽤就是把数据帧从 RingBuffer 上取下来。为什么需要两个函数呢?因为有可能帧要占多个 RingBuffer,所以是在⼀个循环中获取的,直到帧尾部。获取下来的⼀个数据帧⽤⼀个 sk_buff 来表示。收取完数据以后,对其进⾏⼀些校验,然后开始设置 sbk 变量的 timestamp, VLAN id, protocol 等字段。//file: net/core/dev.c gro_result_t napi_gro_receive(struct napi_struct *napi, struct sk_buff *skb) { skb_gro_reset_offset(skb); return napi_skb_finish(dev_gro_receive(napi, skb), skb); }dev_gro_receive 这个函数代表的是⽹卡 GRO 特性,可以简单理解成把相关的⼩包合并成⼀个⼤包就⾏,⽬的是减少传送给⽹络栈的包数,这有助于减少 CPU 的使⽤量。我们暂且忽略,直接看napi_skb_finish , 这个函数主要就是调⽤了 netif_receive_skb 。//file: net/core/dev.c static gro_result_t napi_skb_finish(gro_result_t ret, struct sk_buff *skb) { switch (ret) { case GRO_NORMAL: if (netif_receive_skb(skb)) ret = GRO_DROP; break; ...... }在 netif_receive_skb 中,数据包将被送到协议栈中。3. ⽹络协议栈处理 netif_receive_skb 函数会根据包的协议,假如是 udp 包,会将包依次送到 ip_rcv(), udp_rcv() 协议处理函数中进⾏处理。//file: net/core/dev.c int netif_receive_skb(struct sk_buff *skb) { //RPS处理逻辑,先忽略 ...... return __netif_receive_skb(skb); } static int __netif_receive_skb(struct sk_buff *skb) { ...... ret = __netif_receive_skb_core(skb, false); } static int __netif_receive_skb_core(struct sk_buff *skb, bool pfmemalloc) { ...... //pcap逻辑,这⾥会将数据送⼊抓包点。tcpdump就是从这个⼊⼝获取包的 list_for_each_entry_rcu(ptype, &ptype_all, list) { if (!ptype->dev || ptype->dev == skb->dev) { if (pt_prev) ret = deliver_skb(skb, pt_prev, orig_dev); pt_prev = ptype; } } ...... list_for_each_entry_rcu(ptype, &ptype_base[ntohs(type) & PTYPE_HASH_MASK], list) { if (ptype->type == type && (ptype->dev == null_or_dev || ptype->dev == skb->dev || ptype->dev == orig_dev)) { if (pt_prev) ret = deliver_skb(skb, pt_prev, orig_dev); pt_prev = ptype; } } }__netif_receive_skb_core 取出 protocol,它会从数据包中取出协议信息,然后遍历注册在这个协议上的回调函数列表。//file: net/core/dev.c static inline int deliver_skb(struct sk_buff *skb, struct packet_type *pt_prev, struct net_device *orig_dev) { ...... return pt_prev->func(skb, skb->dev, pt_prev, orig_dev); }pt_prev->func 这⼀⾏就调⽤到了协议层注册的处理函数了。对于 ip 包来讲,就会进⼊到 ip_rcv(如果是arp包的话,会进⼊到arp_rcv)。4. IP 协议层处理//file: net/ipv4/ip_input.c int ip_rcv(struct sk_buff *skb, struct net_device *dev, struct packet_type *pt, struct net_device *orig_dev) { ...... return NF_HOOK(NFPROTO_IPV4, NF_INET_PRE_ROUTING, skb, dev, NULL, ip_rcv_finish); }这⾥ NF_HOOK 是⼀个钩⼦函数,当执⾏完注册的钩⼦后就会执⾏到最后⼀个参数指向的函数ip_rcv_finish 。static int ip_rcv_finish(struct sk_buff *skb) { ...... if (!skb_dst(skb)) { int err = ip_route_input_noref(skb, iph->daddr, iph->saddr, iph->tos, skb->dev); ... } ...... return dst_input(skb); }ip_route_input_noref 看到它⼜调⽤了 ip_route_input_mc 。 在 ip_route_input_mc中,函数 ip_local_deliver 被赋值给了 dst.input//file: net/ipv4/route.c static int ip_route_input_mc(struct sk_buff *skb, __be32 daddr, __be32 saddr, u8 tos, struct net_device *dev, int our) { if (our) { rth->dst.input= ip_local_deliver; rth->rt_flags |= RTCF_LOCAL; } }ip_rcv_finish 中的 return dst_input(skb)/* Input packet from network to transport. */ static inline int dst_input(struct sk_buff *skb) { return skb_dst(skb)->input(skb); }skb_dst(skb)->input 调⽤的 input ⽅法就是路由⼦系统赋的 ip_local_deliver。//file: net/ipv4/ip_input.c int ip_local_deliver(struct sk_buff *skb) { /* * Reassemble IP fragments. */ if (ip_is_fragment(ip_hdr(skb))) { if (ip_defrag(skb, IP_DEFRAG_LOCAL_DELIVER)) return 0; } return NF_HOOK(NFPROTO_IPV4, NF_INET_LOCAL_IN, skb, skb->dev, NULL, ip_local_deliver_finish); } static int ip_local_deliver_finish(struct sk_buff *skb) { ...... int protocol = ip_hdr(skb)->protocol; const struct net_protocol *ipprot; ipprot = rcu_dereference(inet_protos[protocol]); if (ipprot != NULL) { ret = ipprot->handler(skb); } }net_protos 中保存着 tcp_v4_rcv() 和 udp_rcv() 的函数地址。这⾥将会根据包中的协议类型选择进⾏分发,在这⾥ skb 包将会进⼀步被派送到更上层的协议中, udp 和 tcp。{/collapse}
How to receive a network packet in Linux {collapse}{collapse-item label=" 一、简介 " open}在TCP/IP ⽹络分层模型⾥,整个协议栈被分成了物理层、链路层、⽹络层,传输层和应⽤层。物理层对应的是⽹卡和⽹线,应⽤层对应的是我们常⻅的 Nginx,FTP 等等各种应⽤。Linux 实现的是链路层、⽹络层和传输层这三层。在 Linux 内核实现中,链路层协议靠⽹卡驱动来实现,内核协议栈来实现⽹络层和传输层。内核对更上层的应⽤层提供 socket 接⼝来供⽤户进程访问。在 Linux 的源代码中,⽹络设备驱动对应的逻辑位于 driver/net/ethernet , 其中 intel 系列⽹卡的驱动在 driver/net/ethernet/intel ⽬录下。协议栈模块代码位于 kernel 和 net ⽬录。{lamp/}此Linux中断处理函数是分上半部和下半部的。上半部是只进⾏最简单的⼯作,快速处理然后释放 CPU ,接着 CPU 就可以允许其它中断进来。剩下将绝⼤部分的⼯作都放到下半部中。2.4 以后的内核版本采⽤的下半部实现⽅式是软中断,由 ksoftirqd 内核线程全权处理。和硬中断不同的是,硬中断是通过给 CPU 物理引脚施加电压变化,⽽软中断是通过给内存中的⼀个变量的⼆进制值以通知软中断处理程序。当⽹卡上收到数据以后,Linux 中第⼀个⼯作的模块是⽹络驱动。 ⽹络驱动会以 DMA 的⽅式把⽹卡上收到的帧写到内存⾥。再向 CPU 发起⼀个中断,以通知 CPU 有数据到达。第⼆,当 CPU 收到中断请求后,会去调⽤⽹络驱动注册的中断处理函数。 ⽹卡的中断处理函数并不做过多⼯作,发出软中断请求,然后尽快释放 CPU。ksoftirqd 检测到有软中断请求到达,调⽤ poll 开始轮询收包,收到后交由各级协议栈处理。对于 udp 包来说,会被放到⽤户 socket 的接收队列中。{/collapse-item}{collapse-item label=" 二、linux启动 " open} 1. 创建ksoftirqd内核进程 系统初始化的时候在 kernel/smpboot.c中调⽤了 smpboot_register_percpu_thread, 该函数进⼀步会执⾏到 spawn_ksoftirqd(位于kernel/softirq.c)来创建出 softirqd 进程。//file: kernel/softirq.c static struct smp_hotplug_thread softirq_threads = { .store = &ksoftirqd, .thread_should_run = ksoftirqd_should_run, .thread_fn = run_ksoftirqd, .thread_comm = "ksoftirqd/%u", }; static __init int spawn_ksoftirqd(void) { register_cpu_notifier(&cpu_nfb); BUG_ON(smpboot_register_percpu_thread(&softirq_threads)); return 0; } early_initcall(spawn_ksoftirqd);2. 网络子系统初始化 //file: net/core/dev.c static int __init net_dev_init(void) { ...... for_each_possible_cpu(i) { struct softnet_data *sd = &per_cpu(softnet_data, i); memset(sd, 0, sizeof(*sd)); skb_queue_head_init(&sd->input_pkt_queue); skb_queue_head_init(&sd->process_queue); sd->completion_queue = NULL; INIT_LIST_HEAD(&sd->poll_list); ...... } ...... open_softirq(NET_TX_SOFTIRQ, net_tx_action); open_softirq(NET_RX_SOFTIRQ, net_rx_action); } subsys_initcall(net_dev_init);2.1 linux 内核通过调⽤ subsys_initcall 来初始化各个⼦系统,在源代码⽬录⾥你可以 grep 出许多对这个函数的调⽤。2.2 网络子系统初始化的时候会为每个 CPU 都申请⼀个 softnet_data 数据结构,在这个数据结构⾥的poll_list 是等待驱动程序将其 poll 函数注册进来。2.3 open_softirq 注册了每⼀种软中断都注册⼀个处理函数, NET_TX_SOFTIRQ 的处理函数为net_tx_action,NET_RX_SOFTIRQ 的为 net_rx_action。open_softirq 注册的⽅式是记录在 softirq_vec 变量⾥的。ksoftirqd 线程收到软中断的时候,也会使⽤这个变量来找到每⼀种软中断对应的处理函数。3. 协议栈注册 内核实现了网络层的IP协议、传输层的TCP协议和UDP协议,这些协议对应的实现函数分别是 ip_rcv(), tcp_v4_rcv()和 udp_rcv()。内核是通过注册的⽅式来实现的, Linux 内核中的 fs_initcall 和 subsys_initcall 类似,也是初始化模块的⼊⼝。 fs_initcall 调⽤ inet_init 后开始⽹络协议栈注册。 通过 inet_init ,将这些函数注册到了 inet_protos 和 ptype_base 数据结构中了。//file: net/ipv4/af_inet.c static struct packet_type ip_packet_type __read_mostly = { .type = cpu_to_be16(ETH_P_IP), .func = ip_rcv, }; static const struct net_protocol udp_protocol = { .handler = udp_rcv, .err_handler = udp_err, .no_policy = 1, .netns_ok = 1, }; static const struct net_protocol tcp_protocol = { .early_demux = tcp_v4_early_demux, .handler = tcp_v4_rcv, .err_handler = tcp_v4_err, .no_policy = 1, .netns_ok = 1, }; static int __init inet_init(void) { ...... if (inet_add_protocol(&icmp_protocol, IPPROTO_ICMP) < 0) pr_crit("%s: Cannot add ICMP protocol\n", __func__); if (inet_add_protocol(&udp_protocol, IPPROTO_UDP) < 0) pr_crit("%s: Cannot add UDP protocol\n", __func__); if (inet_add_protocol(&tcp_protocol, IPPROTO_TCP) < 0) pr_crit("%s: Cannot add TCP protocol\n", __func__); ...... dev_add_pack(&ip_packet_type); }inet_protos 记录着 udp,tcp 的处理函数地址,ptype_base 存储着 ip_rcv() 函数的处理地址4. ⽹卡驱动初始化 每⼀个驱动程序(不仅仅只是⽹卡驱动)会使⽤ module_init 向内核注册⼀个初始化函数,当驱动被加载时,内核会调⽤这个函数。//file: drivers/net/ethernet/intel/igb/igb_main.c static struct pci_driver igb_driver = { .name = igb_driver_name, .id_table = igb_pci_tbl, .probe = igb_probe, .remove = igb_remove, ...... }; static int __init igb_init_module(void) { ...... ret = pci_register_driver(&igb_driver); return ret; }第2步中驱动probe让驱动处于ready第5步中⽹卡驱动实现了 ethtool 所需要的接⼝,也在这⾥注册完成函数地址的注册。当ethtool 发起⼀个系统调⽤,内核会找到对应操作回调函数第6步注册的 igb_netdev_ops 中包含的是 igb_open 等函数,该函数在⽹卡被启动的时候会被调⽤5. 启动⽹卡 当上⾯的初始化都完成以后,就可以启动⽹卡了。//file: drivers/net/ethernet/intel/igb/igb_main.c static int __igb_open(struct net_device *netdev, bool resuming) { /* allocate transmit descriptors */ err = igb_setup_all_tx_resources(adapter); /* allocate receive descriptors */ err = igb_setup_all_rx_resources(adapter); /* 注册中断处理函数 */ err = igb_request_irq(adapter); if (err) goto err_req_irq; /* 启⽤NAPI */ for (i = 0; i < adapter->num_q_vectors; i++) napi_enable(&(adapter->q_vector[i]->napi)); ...... }{/collapse-item}{collapse-item label=" 二、收包流程 " open} 1. 硬中断处理 ⾸先当数据帧从⽹线到达⽹卡上的时候,第⼀站是⽹卡的接收队列。⽹卡在分配给⾃⼰的 RingBuffer中寻找可⽤的内存位置,找到后 DMA 引擎会把数据 DMA 到⽹卡之前关联的内存⾥,这个时候 CPU都是⽆感的。当 DMA 操作完成以后,⽹卡会向 CPU 发起⼀个硬中断,通知 CPU 有数据到达。2. ksoftirqd 内核线程处理软中断 内核线程初始化的时候,我们介绍了 ksoftirqd 中两个线程函数 ksoftirqd_should_run 和run_ksoftirqd 。static int ksoftirqd_should_run(unsigned int cpu) { return local_softirq_pending(); } #define local_softirq_pending() \ __IRQ_STAT(smp_processor_id(), __softirq_pending)这⾥看到和硬中断中调⽤了同⼀个函数 local_softirq_pending 。使⽤⽅式不同的是硬中断位置是为了写⼊标记,这⾥仅仅只是读取。如果硬中断中设置了 NET_RX_SOFTIRQ ,这⾥⾃然能读取的到。static void run_ksoftirqd(unsigned int cpu) { local_irq_disable(); if (local_softirq_pending()) { __do_softirq(); rcu_note_context_switch(cpu); local_irq_enable(); cond_resched(); return; } local_irq_enable(); }在 __do_softirq 中,判断根据当前 CPU 的软中断类型,调⽤其注册的 action ⽅法。asmlinkage void __do_softirq(void) { do { if (pending & 1) { unsigned int vec_nr = h - softirq_vec; int prev_count = preempt_count(); ... trace_softirq_entry(vec_nr); h->action(h); trace_softirq_exit(vec_nr); ... } h++; pending >>= 1; } while (pending); }硬中断中设置软中断标记,和 ksoftirq 的判断是否有软中断到达,都是基于smp_processor_id() 的。这意味着只要硬中断在哪个 CPU 上被响应,那么软中断也是在这个 CPU 上处理的。如果你发现你的 Linux 软中断 CPU 消耗都集中在⼀个核上的话,做法是要把调整硬中断的 CPU 亲和性,来将硬中断打散到不同的 CPU 核上去。//file:net/core/dev.c static void net_rx_action(struct softirq_action *h) { struct softnet_data *sd = &__get_cpu_var(softnet_data); unsigned long time_limit = jiffies + 2; int budget = netdev_budget; void *have; local_irq_disable(); while (!list_empty(&sd->poll_list)) { ...... n = list_first_entry(&sd->poll_list, struct napi_struct, poll_list); work = 0; if (test_bit(NAPI_STATE_SCHED, &n->state)) { work = n->poll(n, weight); trace_napi_poll(n); } budget -= work;net_rx_action } }函数开头的 time_limit 和 budget 是⽤来控制 net_rx_action 函数主动退出的,⽬的是保证⽹络包的接收不霸占 CPU 不放。 等下次⽹卡再有硬中断过来的时候再处理剩下的接收数据包。其中 budget 可以通过内核参数调整。 这个函数中剩下的核⼼逻辑是获取到当前 CPU 变量 softnet_data,对其 poll_list进⾏遍历, 然后执⾏到⽹卡驱动注册到的 poll 函数。对于 igb ⽹卡来说,就是 igb 驱动⾥的igb_poll 函数了。/** * igb_poll - NAPI Rx polling callback * @napi: napi polling structure * @budget: count of how many packets we should handle **/ static int igb_poll(struct napi_struct *napi, int budget) { ... if (q_vector->tx.ring) clean_complete = igb_clean_tx_irq(q_vector); if (q_vector->rx.ring) clean_complete &= igb_clean_rx_irq(q_vector, budget); ... }在读取操作中, igb_poll 的重点⼯作是对 igb_clean_rx_irq 的调⽤。static bool igb_clean_rx_irq(struct igb_q_vector *q_vector, const int budget) { ... do { /* retrieve a buffer from the ring */ skb = igb_fetch_rx_buffer(rx_ring, rx_desc, skb); /* fetch next buffer in frame if non-eop */ if (igb_is_non_eop(rx_ring, rx_desc)) continue; } /* verify the packet layout is correct */ if (igb_cleanup_headers(rx_ring, rx_desc, skb)) { skb = NULL; continue; } /* populate checksum, timestamp, VLAN, and protocol */ igb_process_skb_fields(rx_ring, rx_desc, skb); napi_gro_receive(&q_vector->napi, skb); }igb_fetch_rx_buffer 和 igb_is_non_eop 的作⽤就是把数据帧从 RingBuffer 上取下来。为什么需要两个函数呢?因为有可能帧要占多个 RingBuffer,所以是在⼀个循环中获取的,直到帧尾部。获取下来的⼀个数据帧⽤⼀个 sk_buff 来表示。收取完数据以后,对其进⾏⼀些校验,然后开始设置 sbk 变量的 timestamp, VLAN id, protocol 等字段。//file: net/core/dev.c gro_result_t napi_gro_receive(struct napi_struct *napi, struct sk_buff *skb) { skb_gro_reset_offset(skb); return napi_skb_finish(dev_gro_receive(napi, skb), skb); }dev_gro_receive 这个函数代表的是⽹卡 GRO 特性,可以简单理解成把相关的⼩包合并成⼀个⼤包就⾏,⽬的是减少传送给⽹络栈的包数,这有助于减少 CPU 的使⽤量。我们暂且忽略,直接看napi_skb_finish , 这个函数主要就是调⽤了 netif_receive_skb 。//file: net/core/dev.c static gro_result_t napi_skb_finish(gro_result_t ret, struct sk_buff *skb) { switch (ret) { case GRO_NORMAL: if (netif_receive_skb(skb)) ret = GRO_DROP; break; ...... }在 netif_receive_skb 中,数据包将被送到协议栈中。3. ⽹络协议栈处理 netif_receive_skb 函数会根据包的协议,假如是 udp 包,会将包依次送到 ip_rcv(), udp_rcv() 协议处理函数中进⾏处理。//file: net/core/dev.c int netif_receive_skb(struct sk_buff *skb) { //RPS处理逻辑,先忽略 ...... return __netif_receive_skb(skb); } static int __netif_receive_skb(struct sk_buff *skb) { ...... ret = __netif_receive_skb_core(skb, false); } static int __netif_receive_skb_core(struct sk_buff *skb, bool pfmemalloc) { ...... //pcap逻辑,这⾥会将数据送⼊抓包点。tcpdump就是从这个⼊⼝获取包的 list_for_each_entry_rcu(ptype, &ptype_all, list) { if (!ptype->dev || ptype->dev == skb->dev) { if (pt_prev) ret = deliver_skb(skb, pt_prev, orig_dev); pt_prev = ptype; } } ...... list_for_each_entry_rcu(ptype, &ptype_base[ntohs(type) & PTYPE_HASH_MASK], list) { if (ptype->type == type && (ptype->dev == null_or_dev || ptype->dev == skb->dev || ptype->dev == orig_dev)) { if (pt_prev) ret = deliver_skb(skb, pt_prev, orig_dev); pt_prev = ptype; } } }__netif_receive_skb_core 取出 protocol,它会从数据包中取出协议信息,然后遍历注册在这个协议上的回调函数列表。//file: net/core/dev.c static inline int deliver_skb(struct sk_buff *skb, struct packet_type *pt_prev, struct net_device *orig_dev) { ...... return pt_prev->func(skb, skb->dev, pt_prev, orig_dev); }pt_prev->func 这⼀⾏就调⽤到了协议层注册的处理函数了。对于 ip 包来讲,就会进⼊到 ip_rcv(如果是arp包的话,会进⼊到arp_rcv)。4. IP 协议层处理//file: net/ipv4/ip_input.c int ip_rcv(struct sk_buff *skb, struct net_device *dev, struct packet_type *pt, struct net_device *orig_dev) { ...... return NF_HOOK(NFPROTO_IPV4, NF_INET_PRE_ROUTING, skb, dev, NULL, ip_rcv_finish); }这⾥ NF_HOOK 是⼀个钩⼦函数,当执⾏完注册的钩⼦后就会执⾏到最后⼀个参数指向的函数ip_rcv_finish 。static int ip_rcv_finish(struct sk_buff *skb) { ...... if (!skb_dst(skb)) { int err = ip_route_input_noref(skb, iph->daddr, iph->saddr, iph->tos, skb->dev); ... } ...... return dst_input(skb); }ip_route_input_noref 看到它⼜调⽤了 ip_route_input_mc 。 在 ip_route_input_mc中,函数 ip_local_deliver 被赋值给了 dst.input//file: net/ipv4/route.c static int ip_route_input_mc(struct sk_buff *skb, __be32 daddr, __be32 saddr, u8 tos, struct net_device *dev, int our) { if (our) { rth->dst.input= ip_local_deliver; rth->rt_flags |= RTCF_LOCAL; } }ip_rcv_finish 中的 return dst_input(skb)/* Input packet from network to transport. */ static inline int dst_input(struct sk_buff *skb) { return skb_dst(skb)->input(skb); }skb_dst(skb)->input 调⽤的 input ⽅法就是路由⼦系统赋的 ip_local_deliver。//file: net/ipv4/ip_input.c int ip_local_deliver(struct sk_buff *skb) { /* * Reassemble IP fragments. */ if (ip_is_fragment(ip_hdr(skb))) { if (ip_defrag(skb, IP_DEFRAG_LOCAL_DELIVER)) return 0; } return NF_HOOK(NFPROTO_IPV4, NF_INET_LOCAL_IN, skb, skb->dev, NULL, ip_local_deliver_finish); } static int ip_local_deliver_finish(struct sk_buff *skb) { ...... int protocol = ip_hdr(skb)->protocol; const struct net_protocol *ipprot; ipprot = rcu_dereference(inet_protos[protocol]); if (ipprot != NULL) { ret = ipprot->handler(skb); } }net_protos 中保存着 tcp_v4_rcv() 和 udp_rcv() 的函数地址。这⾥将会根据包中的协议类型选择进⾏分发,在这⾥ skb 包将会进⼀步被派送到更上层的协议中, udp 和 tcp。{/collapse}