学习teamtalk服务端源码,记录下线程池的实现。
主要是实现的类分为任务类(抽象类)、线程池类、工作线程类、线程同步类。
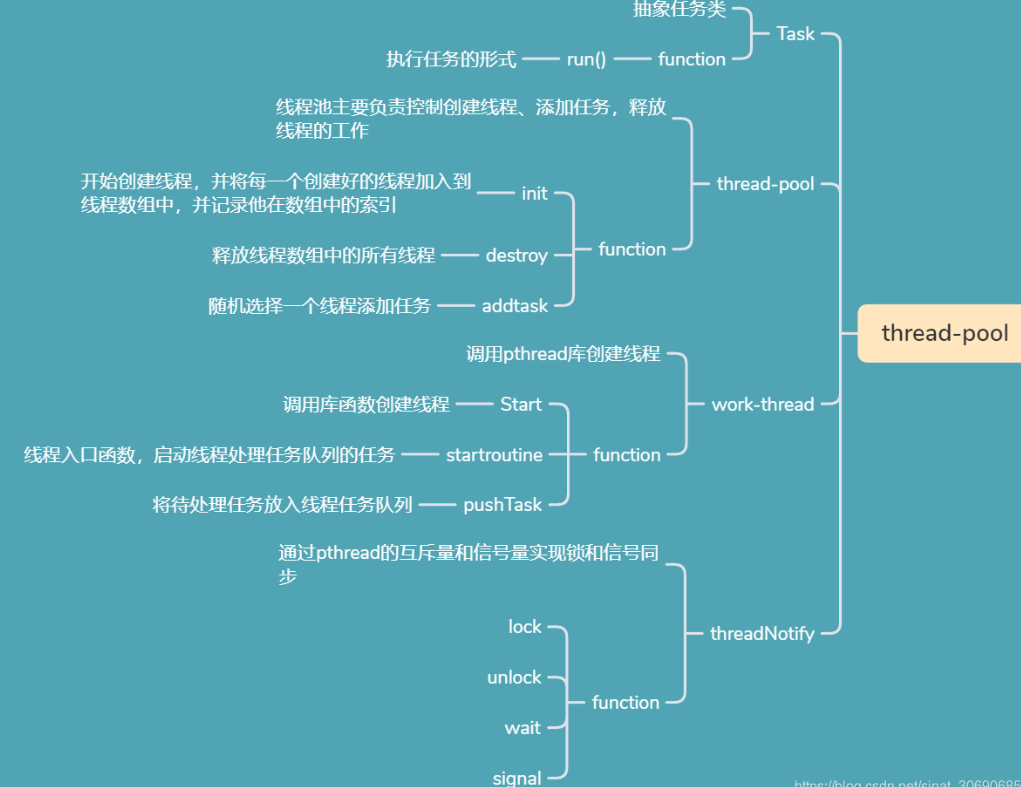
Task抽象任务类 虚基类为了能够处理不同任务
#ifndef __TASK_H__
#define __TASK_H__
class CTask {
public:
CTask(){}
virtual ~CTask(){}
virtual void run() = 0;
private:
};
#endif /*defined(__TASK_H__) */线程池类threadPool
init初始化并启动工作线程
int CThreadPool::Init(uint32_t worker_size)
{
m_worker_size = worker_size;
m_worker_list = new CWorkerThread [m_worker_size];
if (!m_worker_list) {
return 1;
}
for (uint32_t i = 0; i < m_worker_size; i++) {
m_worker_list[i].SetThreadIdx(i);
m_worker_list[i].Start();
}
return 0;
}工作线程创建线程,遍历任务队列并处理。这里遍历任务队列的方式和遍历redis空闲连接队列一样,用一个锁和信号量优雅地等待任务。
void* CWorkerThread::StartRoutine(void* arg)
{
CWorkerThread* pThread = (CWorkerThread*)arg;
pThread->Execute();
return NULL;
}
void CWorkerThread::Start()
{
(void)pthread_create(&m_thread_id, NULL, StartRoutine, this);
}
void CWorkerThread::Execute()
{
while (true) {
m_thread_notify.Lock();
// put wait in while cause there can be spurious wake up (due to signal/ENITR)
while (m_task_list.empty()) {
m_thread_notify.Wait();
}
CTask* pTask = m_task_list.front();
m_task_list.pop_front();
m_thread_notify.Unlock();
pTask->run();
delete pTask;
m_task_cnt++;
//log("%d have the execute %d task\n", m_thread_idx, m_task_cnt);
}
}初始化工作做完说一下add task,通过线程池对象添加任务,根据线程在线程数组中的索引随机添加任务到一个随机线程中,调用工作线程的pushtask function,加锁并唤醒等待任务而阻塞的线程解锁。
void CThreadPool::AddTask(CTask* pTask)
{
/*
* select a random thread to push task
* we can also select a thread that has less task to do
* but that will scan the whole thread list and use thread lock to get each task size
*/
uint32_t thread_idx = random() % m_worker_size;
m_worker_list[thread_idx].PushTask(pTask);
}
void CWorkerThread::PushTask(CTask* pTask)
{
m_thread_notify.Lock();
m_task_list.push_back(pTask);
m_thread_notify.Signal();
m_thread_notify.Unlock();
}线程同步类通过封装pthread的互斥量和信号量实现
构造函数负责初始化互斥量和信号量,析构函数负责destroy操作
CThreadNotify::CThreadNotify()
{
pthread_mutexattr_init(&m_mutexattr);
pthread_mutexattr_settype(&m_mutexattr, PTHREAD_MUTEX_RECURSIVE);
pthread_mutex_init(&m_mutex, &m_mutexattr);
pthread_cond_init(&m_cond, NULL);
}
CThreadNotify::~CThreadNotify()
{
pthread_mutexattr_destroy(&m_mutexattr);
pthread_mutex_destroy(&m_mutex);
pthread_cond_destroy(&m_cond);
}实现线程同步lock、unlock、wait、signal
void Lock() { pthread_mutex_lock(&m_mutex); }
void Unlock() { pthread_mutex_unlock(&m_mutex); }
void Wait() { pthread_cond_wait(&m_cond, &m_mutex); }
void Signal() { pthread_cond_signal(&m_cond); }在dbproxy服务中用到了线程池,proxy连接类处理proxy任务时如下:
static CThreadPool g_thread_pool;
int init_proxy_conn(uint32_t thread_num)
{
//省略其余代码
g_thread_pool.Init(thread_num);
}
void CProxyConn::HandlePduBuf(uchar_t* pdu_buf, uint32_t pdu_len)
{
//省略其余代码
CTask* pTask = new CProxyTask(m_uuid, handler, pPdu);
g_thread_pool.AddTask(pTask);
}proxytask继承了task抽象类,并重写了run方法,使用task抽象类可以处理任何任务,代码质量很高。



评论 (0)